- Home
- CORPORATE
- HISTORY
- MISSION - VISION
- OUR SERVICES
- CERTIFICATES
- NEWS FROM OUR COMPANY
- OUR CODE OF ETHICS
- INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RELATIONS
- TRANSACTIONS
- COMPANY RESOURCES
- RESPECT AT THE WORKPLACE AND WORK LIFE
- WORKPLACE SAFETY AND HEALTH
- SCOPE AND RULES OF APPLICATION
- RESOLVING INCOMPATIBILITY
- ETHICAL DISCLOSURE LINES
- PURPOSE AND SCOPE
- OUR RESPONSIBILITIES AS EMPLOYEE
- PRIVACY
- PROCESSING PERSONAL DATA AND PROTECTION POLICY
- HUMAN RESOURCES
- OUR PRODUCTS
- OUR PROJECTS
- CONTACT
Prismatic Air Ducts Technical Information
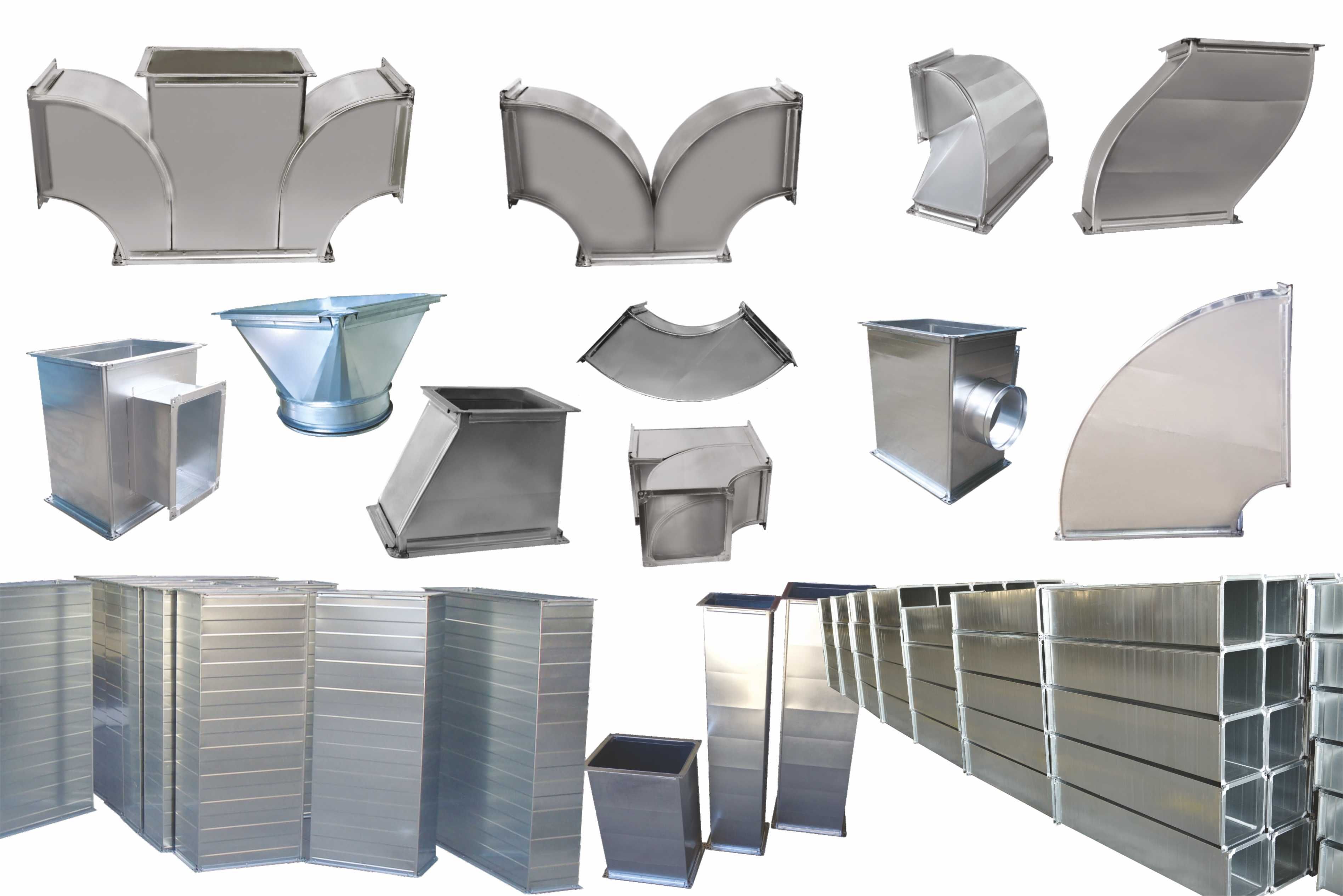

It provides maximum impermeability in prismatic channels compared to other channel types. Fabricated air ducts using special silicon, which reduces air losses at the duct joints to almost zero, are produced in our factory equipped with the latest technology. The material of ducts, elbows, shaped parts and all other branches are produced in accordance with EN 10142 and manufacturing in accordance with TS-EN 1505. Flanges manufactured from special profiles are fixed to the duct by spot welding. Antibacterial mastic is used between the flanges.
- PRISMATIC AIR DUCT TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
- Advantages of Prismatic Air Duct
- About the System
- Dimensions
- Airtightness
- Design
- Tolerances and Deviations
- Labeling
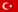
- Table 3
- Hardness
- Table 4
- Ventilation Pipe Area
- Links
- Table 5
- Table 6
-
PRISMATIC AIR DUCT TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
- Its strength ratio is higher than the others.
- It is long lasting and more durable.
- It is produced from galvanized, stainless, aluminum and DKP sheet metal.
- It can be painted in the desired color with electrostatic oven paint.
- Fast and high quality production is done.
-
Advantages of Prismatic Air Duct
- Computer controlled design.
- Minimizing the errors that may occur in workmanship.
- It has an aesthetically beautiful appearance.
- Maximum sealing.
- Quality production.
- Lower costs.
- Ease of assembly.
-
About the System
We offer a production gamut of rectangular ducts and components. The catalog contains rectangular ducts and connections with dimensions in accordance with the PN-EN 1505:2001 (Flat Square Profile Metal Ventilation Ducts and Connections) standard and all standards specified here. The area of ventilation pipes and connections is measured according to the standard DIN 18379 (German Construction Contract Procedures: Part C: General Technical Specifications for Civil Works - Room Ventilation Systems). They are used in low and medium pressure building ventilation and air conditioning systems. Stainless steel or aluminum pipes and connections can also be produced separately on request where higher protection against corrosion is required. Special fittings not included in the catalog are also available based on your drawings.
-
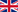
Dimensions
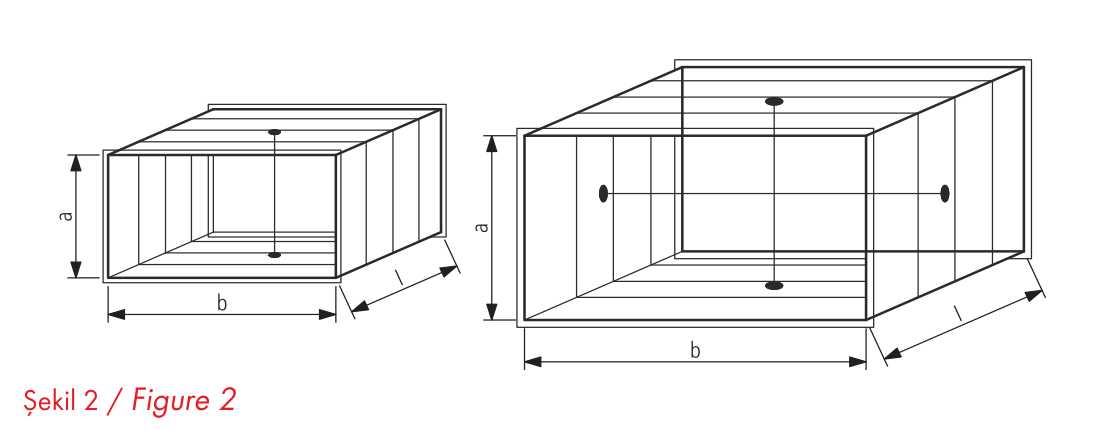
The nominal size traditionally used in the identification and calculation of straight pipes and fittings is equal to the inside dimensions from sides a and b, with a being the visible side. (see figure 1). The side lengths of the small end of the through connector are defined as c and d, with c being the visible side. Size L represents the usable length of straight pipe. For example, size I, which affects the entire length of the piping system, the size that affects the usable length of the fitting. Size I represents the usable length of straight pipe. For example, the size that affects the entire length of the piping system.
-
Airtightness
Ventilation piping as two tightness classes as defined in PN-B-76001 (Ventilation Pipes – Airtightness, Requirements and Test) and PN-EN 1507 (Building Ventilation – Straight Rectangular Ventilation Pipe and Fittings – Pipe Strength and Airtightness Requirements). are produced: tightness class A: for normal typical designs and tightness class B: for designs with higher airtightness.
-
Design
Rectangular ducts and fittings are equipped with sliding and plug-in connections, either welded or clip-on. Pipe and fittings are available in low and medium pressure variants (minimum negative pressure / maximum overpressure): *Design class N (low pressure design): a standard design, ranging from -400 Pa to +1,000 Pa. *Design class S (medium pressure design): -1,000 Pa to 2,500 Pa.
Deviations and sheet metal thickness are selected based on the following criteria:
*Length of the longer side of the straight pipe
*The length of the longest side of the connection section of the connector
The allowable deviation values and minimum sheet metal thicknesses for individual dimensions are given in the table.
-
Tolerances and Deviations
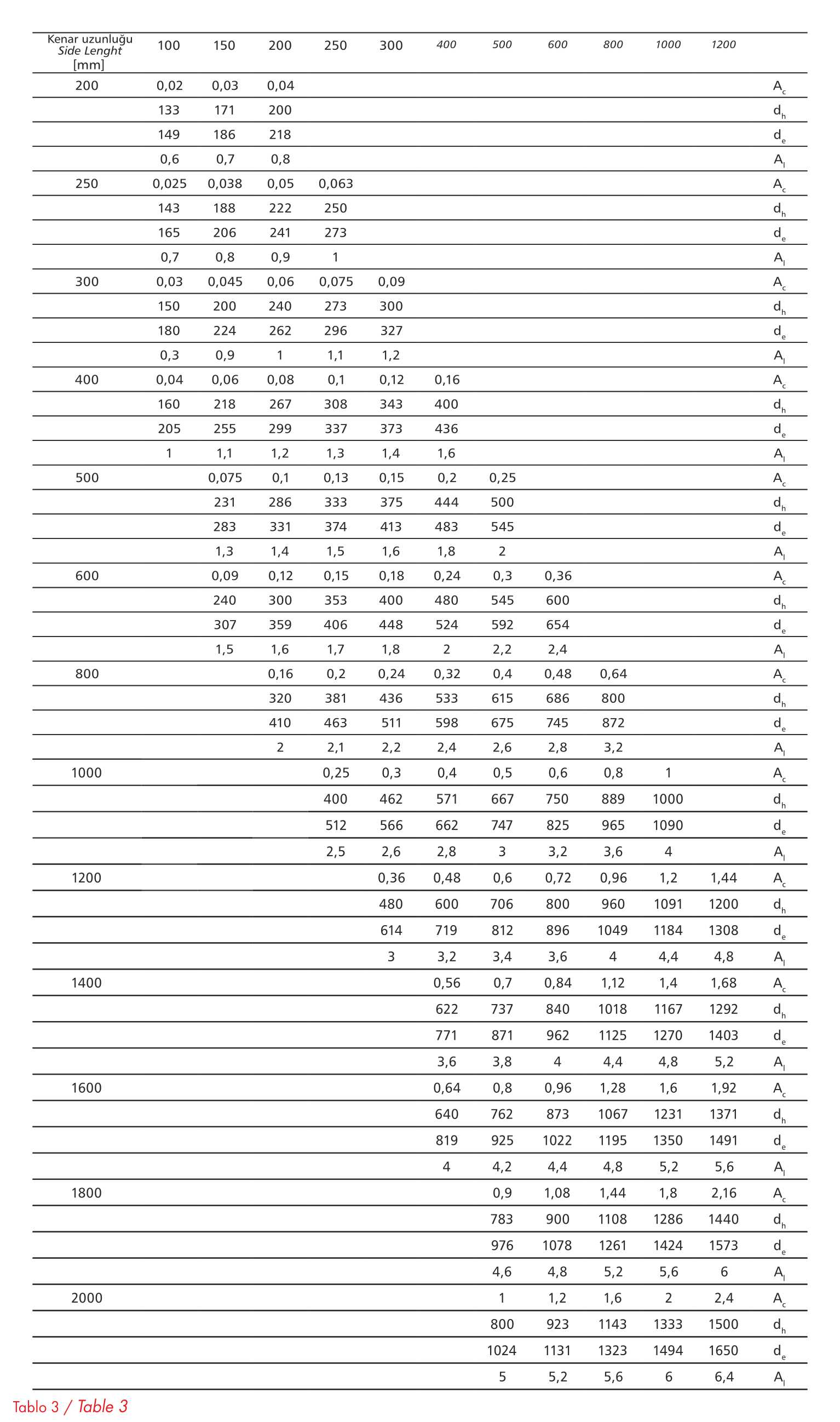
For straight pipes, the L length tolerance is ±0.005L and the angle tolerance is ±2°. Deviations from a,b,c,d,e and f values vary between 0 and -4mm. Pipe sizes including the matching of cross areas, Ac, hydraulic diameter dh, equal diameter and pipe area A per meter are given in table 3.
-
Labeling
KARSAC products are supplied with the B mark of the construction industry, and the product codes comply with the technical specifications in this catalogue.
Rectangular pipes and fittings have the following hygiene certificates.
a) HK/B/1652/03/2007 – For those made of aluminum sheet
b) HK/B/1652/01/2007 – For those made of galvanized or stainless sheet
-
Table 3
Pipe Sizes and values specified in the PN-EN 1505 standard (Flat Rectangular Metal Plate Ventilation Pipes and Fittings).
The cross-sectional area of the product is the area obtained by multiplying the lengths of the sides a and b.
Hydraulic diameter: relative to rectangular pipe, it is the diameter of a round pipe where the pressure drop is the same for similar air flow rates and friction factors.
Formula dh=2 x a x b / a + b
Equivalent diameter: In relation to rectangular pipe, it is the diameter of a round pipe where the pressure drop is the same for similar air flow rates and friction factors.
-
Hardness
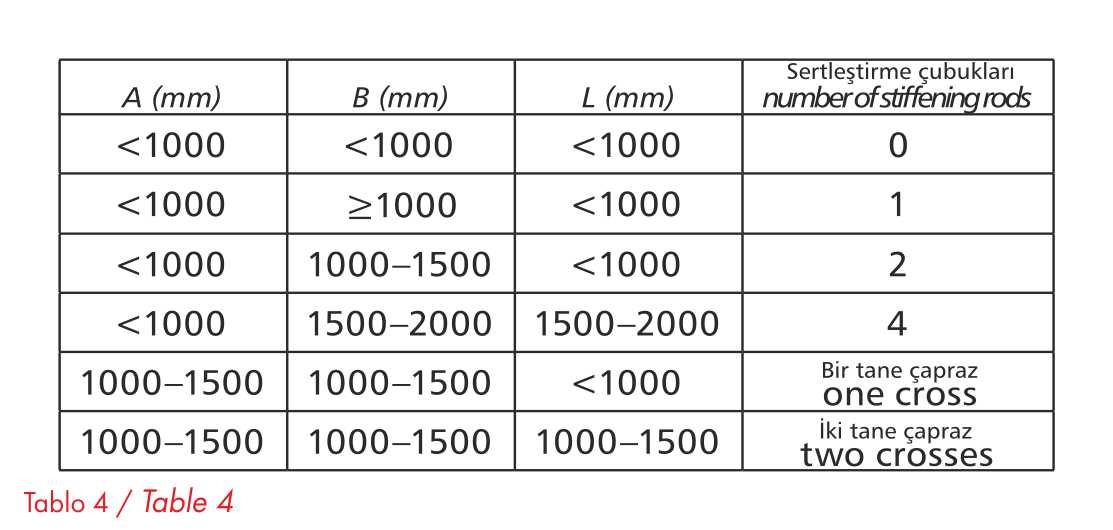
Rectangular pipes and fittings are made even more rigid by cross corrugation of metal sheets. Additionally, the pipes are hardened with galvanized hardening rods as shown in figure 2. Table 4 shows how to increase the hardness of ventilation pipes.
-
Table 4
Increasing the stiffness of ventilation pipes with stiffening rods.
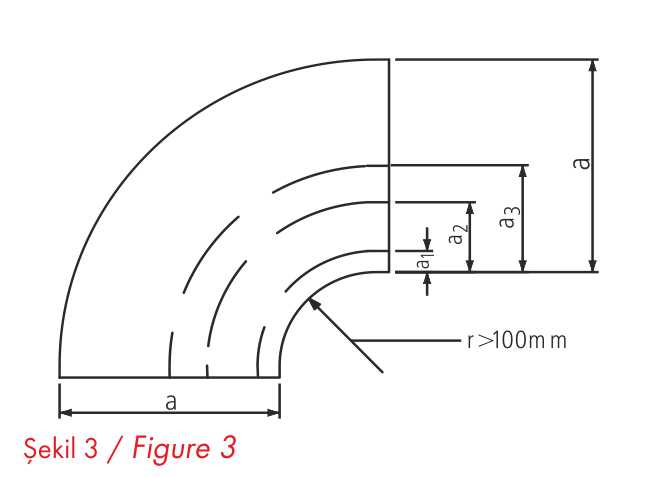
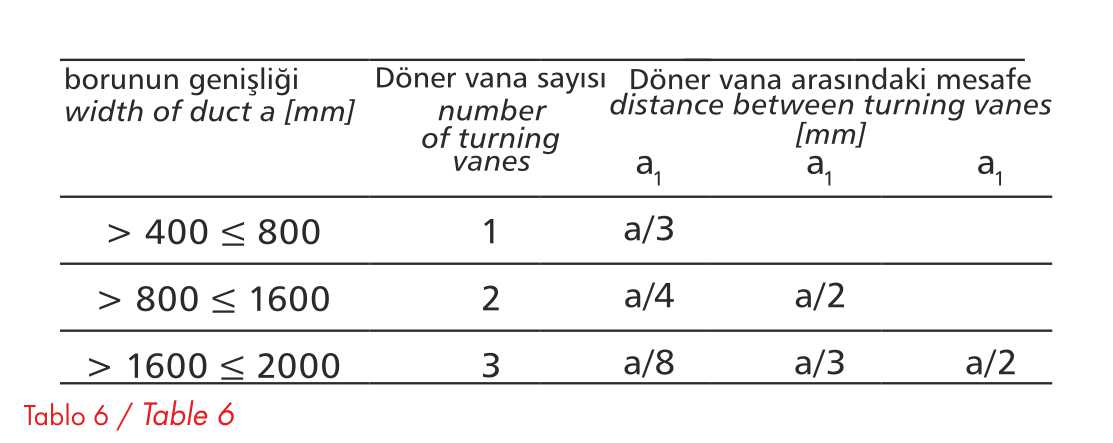
The bends are hardened in rotary valves as specified in the PNEN 1505 standard (Flat Rectangular Metal Plate Ventilation Pipes and Fittings). Bends (elbows) are recommended for systems with low flow rates/pressures and smaller side lengths < 400mm. Rotary valves are not required for bends with an angle < 45°. How to adjust the rotary valves is shown in table 5 and figüre3
-
Ventilation Pipe Area
The area of rectangular ventilation pipes is measured in accordance with the DIN 18379 standard. (German Construction Contracting Procedures. Part C: General Technical Specifications for Civil Works – Room Ventilation Systems). Pipes with an area of less than 1.0 m² are defined as fittings with an area of 1.0 m². Fittings with an area of less than 1.0 m² are defined as fittings with an area of 1.0 m².
-
Links
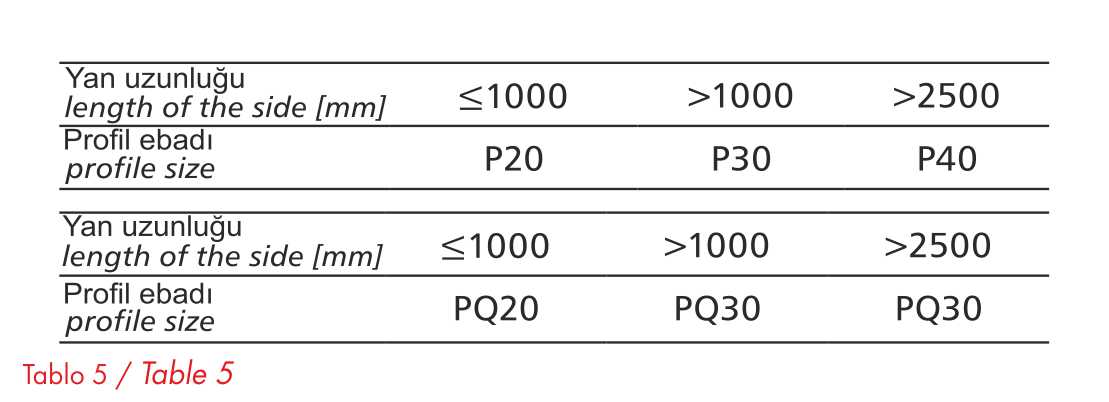
Vent pipes are joined as specified in the PN-B-760012 standard (Metal Plate Ventilation Equipment, Connection of Pipe and Fittings). The metal plate joining profile and angular mounting frames are used to join the ventilation pipes with the rectangular parts of the piping system. The profile size depends on the length of the relevant side. Table 6 shows how to use mounting frames with rectangular pipes and fittings.
-
Table 5
It is shown how to use mounting frames with vent pipes and fittings on standard galvanized sheet metal designs. Corners and closed profiles are sealed with modeling/shaping mortar. Stainless steel mounting frames and corners are generally used for stainless profile pipes and connections, while aluminum mounting frames and corners are used for aluminum pipes and fittings.
-
Table 6
Rotary valves are shown as specified in the PN-EN 1505 standard (Flat Rectangular Metal Plate Ventilation Pipes and Fittings).
© 2025 Karsac | All Rights Reserved. | Created by BWorks